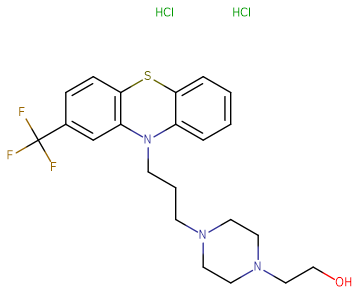
Fluphenazine hydrochloride
CAS No. 146-56-5
Fluphenazine hydrochloride( —— )
Catalog No. M11996 CAS No. 146-56-5
Fluphenazine dihydrochloride is a phenothiazine-class D1DR and D2DR inhibitor.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 50MG | 39 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 47 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 68 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 107 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameFluphenazine hydrochloride
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionFluphenazine dihydrochloride is a phenothiazine-class D1DR and D2DR inhibitor.
-
DescriptionFluphenazine dihydrochloride is a phenothiazine-class D1DR and D2DR inhibitor; used to deliver Fluphenazine to biological systems in studies probing the effects and metabolic fates of this commonly used dopamine antagonist.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayGPCR/G Protein
-
TargetDopamine Receptor
-
RecptorDopamine
-
Research AreaNeurological Disease
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number146-56-5
-
Formula Weight510.44
-
Molecular FormulaC22H28Cl2F3N3OS
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO: 38mg/mL
-
SMILESCl.Cl.OCCN1CCN(CCCN2C3=CC=CC=C3SC3=C2C=C(C=C3)C(F)(F)F)CC1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference



-
Syrosingopine
Syrosingopine has selective depleting effect on brain amines is potentiated by combined treatment with disulfiram or fusaric acid, a dopamine beta-hydroxylase inhibitor.
-
SKF-83566
SKF-83566 is a blood-brain permeable and orally active antagonist of D1-like dopamine receptor and a weaker competitive 5-HT2 receptor antagonist with Ki of 11 nMSKF-83566 caused a concentration-dependent increase in peak single-pulse evoked extracellular DA concentration, with a maximum increase of 65% in 5 μM SKF-83566.?
-
Docosahexaenoic acid...
Docosahexaenoic acid ethyl ester (Ethyl docosahexaenoate) enhances 6-hydroxydopamine-induced neuronal damage by inducing lipid peroxidation in the mouse striatum, and can be used to study oxidative diseases of the retina or neurons.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


